
Conception tips for women with irregular periods
Having irregular cycles may make it more difficult for a woman to become pregnant than it is for a woman with regular cycles. Women with irregular menstrual cycles may be anovulatory (meaning they do not ovulate) or ovulatory (meaning they ovulate).
If you are not ovulating, you will have to take medications to regularise your cycle and injectable fertility drugs to induce ovulation.
If you're ovulating, you may be able to get pregnant without the help of fertility drugs. But since your periods are irregular, predicting ovulation and timing intercourse to up pregnancy chances can be difficult.
Although all women facing menstrual irregularities should seek medical help, there are a few things we can suggest you to do that may help you if you are trying to conceive with irregular periods.
Here’s What You Can Do!!
Maintain a Menstruation Chart:
The first thing you should to if you have irregular periods is to track your periods over the course of 6-7 months. This will help you know how should or how long you periods can vary and when you have heavy and light flows. Although your period are irregular sometimes a pattern emerges. This record can be of great help to your doctor when you seek advice regarding menstrual irregularities later.
Check for signs of ovulation by using your own biological clues.
Women with irregular periods may ovulated less frequently than normal woman. So for instance if Normal women ovulate 12 times in year, women with irregular period may oblate 6 times.
So finding out if you are ovulating or not can help you if you are planning to conceive. Fortunately your body shows certain signs of ovulation that you can track and keep a record of every.
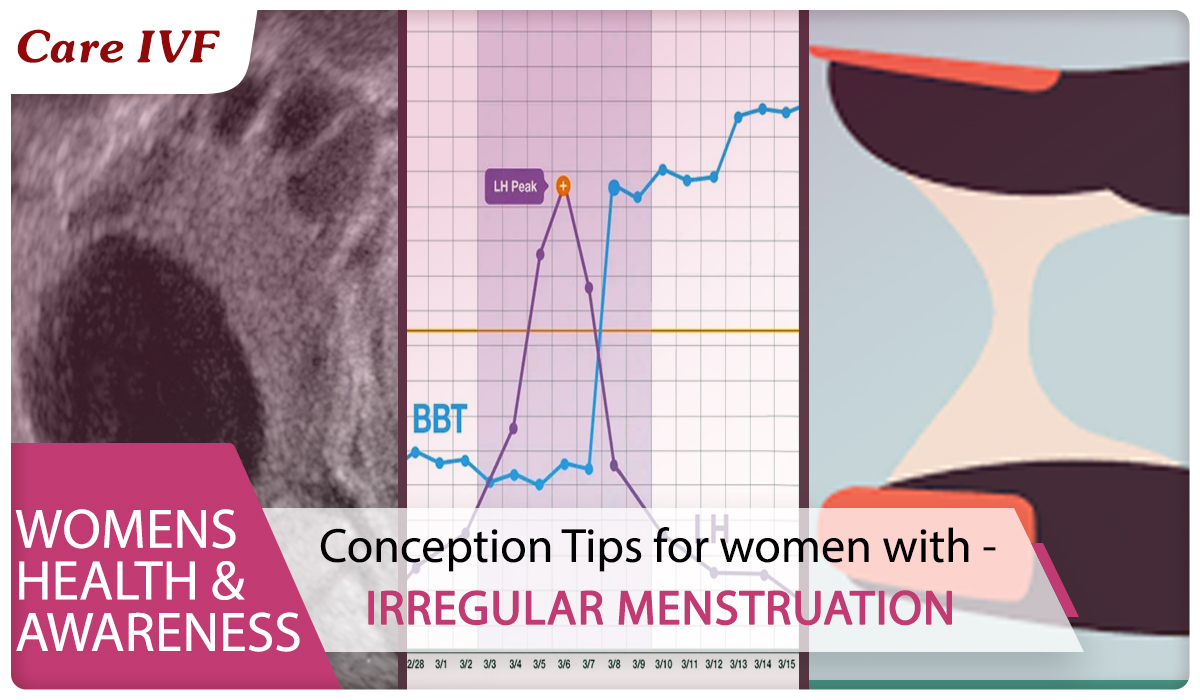
The American pregnancy association recommends Basal body temperature tracking and cervical mucus tracking as basic first line approach for women with period irregularities.
A spike in your basal body temperature
The body experiences a rise in temperature once ovulation starts. So charting you basal body temperature is another way of telling if and when you ovulate. If you are charting the temperature every day, you will notice a sharp spike in basal body temperature on the chart on the day you ovulate.
How to maintain Basal Body temperature chart
- Take your basal body temperature with a basal body thermometer first thing in the morning, before you eat, talk, or even get out of bed.
- Chart your temperature all month long.
- The onset of the ovulation window is expected to change the basal body temperature and that too, quite considerably.
Although this will not tell you when you ovulate in advance as the temperature spikes occurs after you have ovulated, tracking this over a course of few months can help you see a pattern.
Tracking your cervical mucus:
Just before ovulation occurs, the hormone estrogen leads to increased cervical mucus and changes it into a stretchy, viscous-like substance. This helps sperm survive and swim.
Cervical fluid changes throughout your cycle and is an indicator that ovulation is on the way. After your period and as you approach ovulation, cervical fluid secretions develop more fertile characteristics and you should notice a pattern of increasing wetness.
Remember that thin, stretchy clear, egg white-like mucus is considered fertile, as it happens around the time when your egg may be released. This is a sign that ovulation is near.
Tracking cervical mucus changes along with Basal Body temperature chart can be a great help for women with irregular periods who trying to conceive naturally.
Use Ovulation Prediction Kits:
Ovulation predictor kits are fairly accurate at detecting a surge in luteinizing hormone, which triggers ovulation.
We would recommend you to take ovulation tests regularly to know when you will be ovulating. Ovulation usually occurs 24 to 36 hours after LH peak. Two days prior to ovulation leading up to ovulation day and one day after ovulation would be your most fertile time.
How to use LH Test kits?
- LH test kits can be purchased online or form a drug store. It contains a strip that you need to dip into a container of your Urine sample. The strip will show two double lines when the LH surge happens.
- You need to do this test every day till you get a positive result
Ovulation predicting kits may get expensive for women with irregular periods. If you have irregular periods, you may want to wait to use an ovulation predictor kit until you observe other signs of ovulation. If you are already tracking cervical mucus changes, and basal body temperature over past months, correlating both will give you a fair idea of when to start using the LH tests.
Menstrual cycle monitoring via Follicular Scans.
Menstrual cycle monitoring by folliculometry is a sure shot way of determining if and when you are ovulating as it tracks the growth of follicles, identifies pre-ovulatory follicle and also checks if all parameters are optimal for fertilization through a series of scans from day 2 of your period till ovulation.
To know more about the applications of folliculometry and how it can be have help if you are trying to conceive naturally read this article:
In conclusion Irregular periods is a hindrance to conception but with proper guidance and steps, women with irregular periods can conceive naturally or via assisted reproduction. The best approach would be to see a doctor who would guide you regarding this. The doctor will not only ascertain whether you are ovulating or not but also ascertain the cause of the irregularities and according advise you how best to proceed.
If you are facing irregular periods and need conception guidance reach out to our fertility experts by booking an appointment at 033-66-398-600.
Article Tags
About the author

Leave a Comment